 Process
Analysis Toolkit (PAT) 3.5
Help Process
Analysis Toolkit (PAT) 3.5
Help |
A transition is used to describe how the
state of the process changes as the result of some action of the process. It is
composed of six parts. The transition
label is represented as below: select
: selections clocks : <clock guard>[transition
guard]event{program}clockreset: clock. A selection binds a variable, which
appears in clock guard, transition guard, event, program or clock reset parts, in a given range. The
evaluation order of the transition is in the following: first, the transition
guard is checked, followed by the clock guard. When both guards are valid,
the event occurs, in the meantime, the program is updated and the
clock is reset. If transitions labelled with complementary actions over a
common channel, the evaluation order of a channel likes the
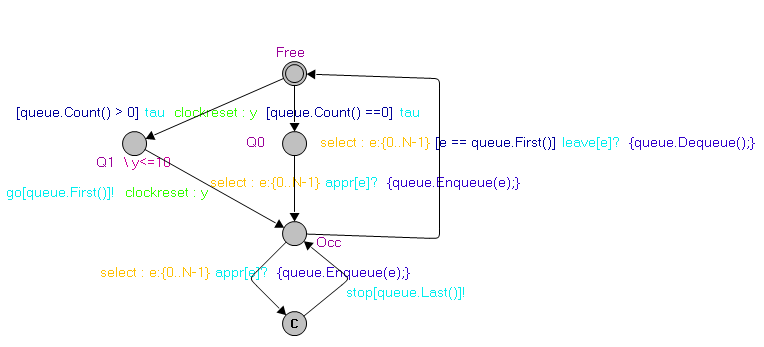
following: In the above
picture, the transition from state Occ to state Free is defined as select : e:{0..N-1} [e == queue.First()]
leave[e]? {queue.Dequeue();}, where queue is an instance of data type Queue
defined as a class in C# language, First() and Dequeue() are functions
defined in the Queue class. The range of variable e is from 0 to N-1, and the value of e in the transition guard and event
should also be in this scope. If Boolean expression e== queue.First() returns true, then if
processes can synchronize over channel leave[e] (value of e should be the same in the transition
guard), in this case, event leave[e]!
occurs, followed by the execution of program queue.Dequeue().
1. channel output guard evaluation and
checking
2. channel output clock guard evaluation and
checking
3. channel output channel name
evaluation
4. channel input channel name
evaluation
5. channel input guard evaluation and
checking
6. channel input clock guard evaluation and
checking
7. channel output program
evaluation
8. channel input program
evaluation.
-
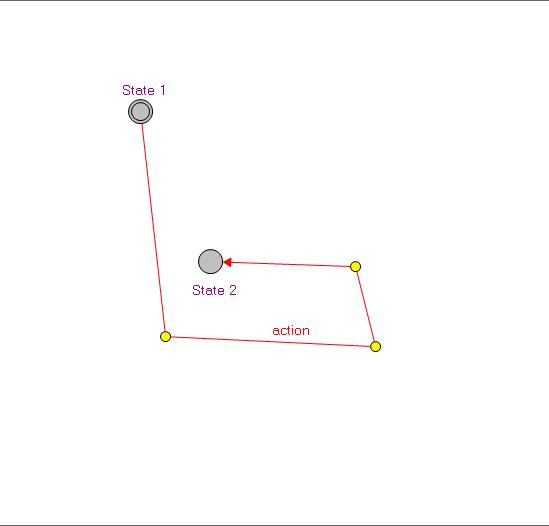
Create Transition: Select the Add Link function then select the first state and the second state. Between selections of the two states, you can click in the canvas to create a new Nail. Nail is a small dot in yellow color. It is used to divide the transition in segments.
- Delete Transition: Select the link then click the Delete function or select Delete function from that link's context menu.
-
Create Nail: Right click on the link and select New Nail.
-
Delete Nail: Select the Nail then select the delete function from the toolbar or its context menu.
-
Move Nail: Select the Nail and drag the nail to the desired position.
Copyright © 2007-2012 Semantic Engineering Pte. Ltd.